SUPPLIERS OF VITAMIN K2 MK4 and MK7
VITAMIN K2 POWDER AND OIL wholesale TO MANUFACTURERS
Falcon Trading International is a USA based wholesale supplier of Vitamin K2 MK4 and MK7. Menatetrenone (MK4) and menaquinone (MK7) are available in various strengths, in oil or powder form. These are top selling products due to their proven effectiveness in the areas of bone and heart health.
WHAT IS VITAMIN K?
Vitamin K is an essential fat soluble compound which is most often used by nutritional manufacturers in the forms of Vitamin K1, Vitamin K2 MK4 and MK7. Vitamin K1 is also known as phylloquinone. Vitamin K2 MK4, and Vitamin K2 MK7 are menaquinones, although MK4 is also classified as menatetrenone.
HOW VITAMIN K2 FUNCTIONS IN THE BODY
Vitamin K2 plays an essential role in carboxylation of glutamic acid to γ-carboxy glutamic acid (Gla). This process allows for coagulation of blood, critical binding of calcium to the bone matrix, removal of calcium from soft tissues such as arteries, and other biological functions.
Each Vitamin K variation, MK4 and MK7, has particular characteristics, effects and applications. Based on some studies, MK4 may be better at protecting tissues from calcium deposits and cancer development. MK7 is more effective in reaching the liver and bones.
Overall, the most common applications are that of bone building and bone preservation relating to osteoporosis, other bone health issues, arterial and cardiovascular health and chronic kidney disease. For a comprehensive overview of the subject see this National Institute of Health Vitamin K2 Fact Sheet for Health Professionals.
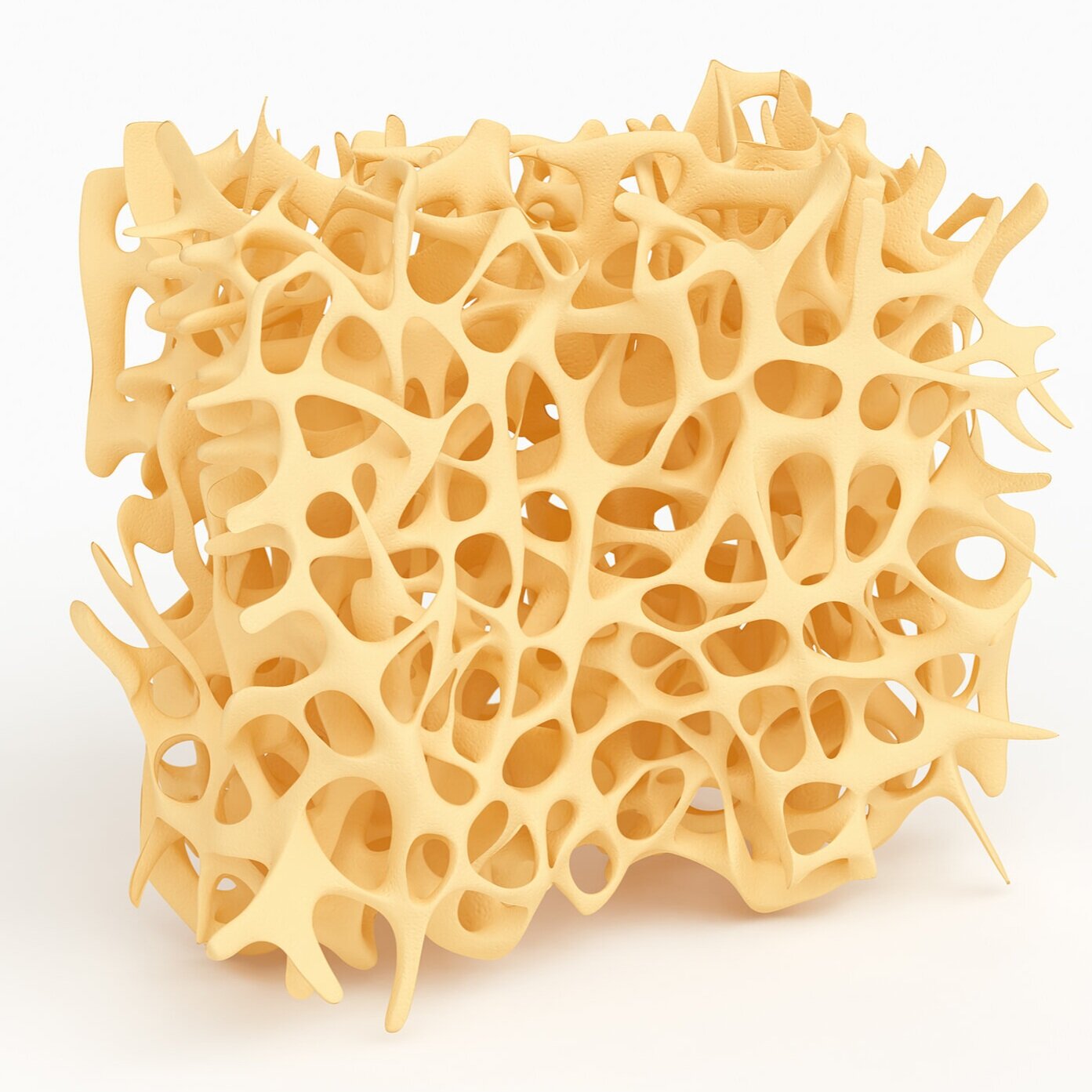
bone basics and the role of Vitamin k2
The human skeleton is a living mass of 206 bones. It regenerates every ten years in an perpetual process of building and rebuilding. Older bone material with microdamage is systematically replaced by new bone as biomineralization occurs. This repair of the bone matrix is made possible by carboxylation of bone gamma-carboxyglutamic acid (Gla).
For carboxylation to occur, the Gla must be activated by Vitamin K2, which allows the Gla containing osteocalcin protein to bind calcium to the hydroxyapetite matrix in the bone. For a more comprehensive explanation of the chemical and physical properties of gamma-carboxyglutamate, PubChem provides detailed information from The National Center for Biotechnology Information.
VITAMIN K2 REDUCES OSTEOPOROSIS FRACTURES
Many studies have indicated that Vitamin K2 plays an important role in maintaining bone mineral density, causing a reduction of incidence of fractures in individuals with osteoporosis. A paper published in the Journal of the American Medical Association, by Sarah Cockayne, MSc; Joy Adamson, PhD; Susan Lanham-New, PhD; et al, reviewed thirteen studies which referenced the effect of Vitamin K2 on bone loss and bone mineral density (BMD).
Twelve of the thirteen studies showed a positive effect of Vitamin K1 (phytonadione) and Vitamin K2 MK4 (menaquinone-4) relating to BMD. Seven of the studies involved fracture outcomes. All seven indicated a benefit of supplementing with MK4.
In the review, they examined studies involving vertebral, non-vertebra and hip fractures, and found the reduction of incidences to be consistent among all fracture types. In the comment section of the review, the authors characterized the results of the 80% reduction in hip fractures to be “particularly striking.” Read the full review entitled Vitamin K and the Prevention of Fractures, as published in the Journal of The American Medical Association.
VITAMIN K2 AND HEART HEALTH
Multiple studies have documented the role of vitamin k2 in improved cardiovascular health through inhibition of vascular calcification. One such 2017 review by Gerry Kurt Schwalfenberg, indicated “significant risk reduction of coronary heart disease, and severe aortic calcification.” This was a seven year study in which more than 4,000 subjects were followed, in categories of high and low Vitamin K2 intake. In this review, although Phylloquinone (Vitamin K1) was found to not be related to coronary outcomes, however vitamin K2 was.
The study also characterized the addition of vitamin K2 as “essential for good bone health.” Also reviewed were the prospects for Vitamin K applications in the areas of diabetes, osteoporosis and cancer. See this comprehensive Vitamin K1 and K2 study, as published in The Journal of Nutrition and Metabolism and PubMed.
CALCIUM AND VITAMIN K2
Calcium is the human body’s most abundant mineral. It is essential for providing structure and hardness to bone mass. It also fortifies the body against osteoporosis and other detrimental bone health issues.
Roughly 1% of calcium in the body is utilized for muscle and blood vessel expansion and contraction, and nerve signaling function. The remaining 99% is directed to bones and teeth. Vitamin K2 is the vehicle that allows calcium ions to be bound and moved from soft tissue, such as arteries, to bone mass where it is needed for remineralization.
Balancing Benefit and Risk from Calcium Supplementation
A possible danger in excessive calcium supplementation may be an increased risk of cardiovascular disease, as several recent studies have concluded. One such study (Xiao et al) considered the effect of calcium supplementation relating to cardiovascular disease.
The study followed large groups of 219,059 men and 169,170 women. It concluded that the men’s group had a cardiovascular death risk factor of 20% more than those taking no calcium supplements. Some other studies have reached conclusions that moderate calcium supplementation has no effect on myocardial infarction or other coronary issues.
An article by John J.B. Anderson, Bridgit Kruszka, et al, published in the Journal of the American Heart Association (JAHA), concluded that “High total calcium intake was associated with a decreased risk of incident atherosclerosis over long-term follow-up, particularly if achieved without supplement use. However, calcium supplement use may increase the risk for incident CAC.”
The article also presented an overview of the methods, the study design, the criteria of dietary intake of participants, and a statistical analysis with multiple charts. For manufacturers of calcium or K2 products, this JAHA link may be very useful.
The JAHA page provides a clickable link reference to other studies which show varying conclusions on the larger question of calcium supplementation, as it relates to cardiovascular and articular health. It is an excellent reference source for manufacturers and formulators to build knowledge when determining product application.
Dietary Calcium Consumption vs. Calcium Supplementation
A common finding of many studies is that calcium from ordinary dietary food sources does not pose a cardiovascular risk, because the calcium levels are lower, and they are assimilated by the body at a slower rate. Calcium loading of excessive amounts entering the body over a short time span may be problematic. For manufacturers utilizing calcium supplementation or considering the benefits of K2 in a product, this subject is well worth researching.
VITAMIN K2 AND REDUCTION OF ARTERIAL CALCIFICATION
Vitamin K2 provides a well defined bodily mechanism which reduces arterial calcification. Matrix Gla Protein, or MGP, along with other Gla proteins in osteocalcin, are dependent on activation by Vitamin K2. Once activated, these proteins bind to calcium, removing it from arteries where it could otherwise lead to cardiovascular problems. This calcium removal mechanism is especially important for elderly adults who may be more prone to Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD), since the kidneys in people with CKD can lose significant ability to filter, which leads to excessive calcification of arteries.
Bioavailability of Vitamin K2 MK4 vs MK7
The bioavailablity of Vitamin K2 varies by type: Vitamin K2 MK4 is absorbed into tissues quickly and has a shorter time span in the body (a matter of hours). Synthesized MK4 is also absorbed less readily than MK7, as it binds to bacteria membranes in the gut. Vitamin K2 MK-7 is much more efficiently absorbed and will remain in the body for several days.